In this blog, we will discuss the geometry of phosphorus pentafluoride, its structure, and some of its properties. We will also discuss whether it is a Lewis acid or not. This blog will provide you with an overview of the geometry of the trigonal bipyramidal structure. We will try to find the answers to our questions related to trigonal bipyramidal. After observation, we will be able to determine the geometry of PF5 and we will be able to know some interesting factors about phosphorus pentafluoride.
What is Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometry?
A trigonal bipyramidal shape establishes when a central atom is surrounded by five atoms in a molecule. In this geometry, atoms are arranged in two planes. Three atoms are in the same plane with bond angles of 120 degrees while the other two atoms are on opposite ends of the molecule. In this geometry bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions.

Some Interesting facts about Trigonal Bipyramidal Geometry
Coordination number in trigonal bipyramidal structure is 5, point group is D3h, polarity is 0 and bond angles are 120 degrees and 90 degrees. They have zero lone pairs with steric number 5. They are non polar in nature. Their hybridization is sp3d.
What is the Geometry of Phosphorus Pentafluoride PF5?
PF5 is a phosphorus halide. It is a toxic and colorless gas that fumes in the air.

The axial and equatorial fluorine atoms rapidly exchange positions because of a low barrier for pseudo-rotation via the berry mechanism. R. Gutowsky noticed the apparent equivalency of the F centers in PF5 and Stephen Berry described the explanation (who also discovered the berry mechanism).
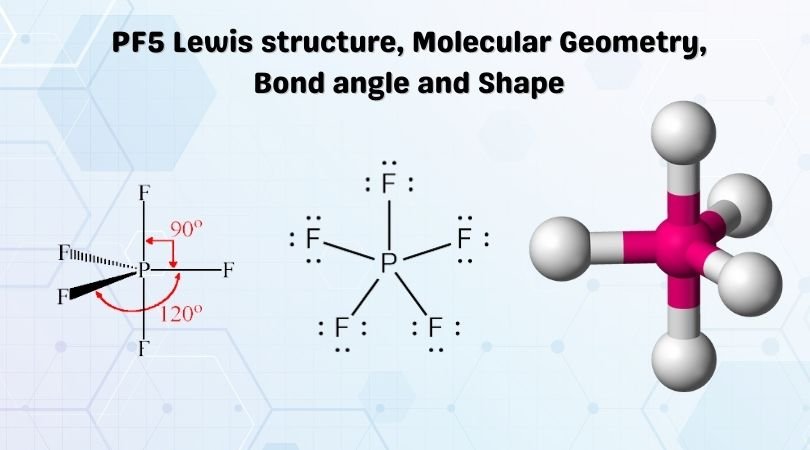
Trigonal bipyramidal geometry of PF5
Single crystal X-ray studies show that the PF5 has trigonal bipyramidal geometry. Phosphorus pentafluoride has 5 regions of electron density around the central phosphorus atom 5 bond pairs and no lone pair. The resulting shape is a trigonal bipyramidal in which three fluorine atoms occupy equatorial and two occupy axial positions. The F-P-F angle between equatorial positions is 120 degrees, and between the axial and equatorial positions, it is 90 degrees.
Is PF5 a Lewis acid?
Yes, PF5 is a Lewis acid. This property is relevant to its ready hydrolysis. A well-studied adduct is PF5 with pyridine. With primary and secondary amines, the adducts convert readily to dimeric amido-bridged derivatives with the formula [PF5 (NR2)]2.
How PF5 was prepared initially?
It was first prepared in 1876 by the fluorination of phosphorus pentachloride using arsenic trifluoride.
3 PCl5 + 5 AsF3 → 3PF5 + AsCl3
Write some properties of PF5
- It has a molar mass of 125.966g/mol.
- Its density is 5.527 kg/m3.
- The melting point of PF5 is -93.78C and the boiling point is -84.6C.
- It is a colorless gas with an unpleasant odor.
- It is non-flammable gas.
- PF5 is a very toxic gas and can cause pulmonary edema.
Conclusion
In trigonal bipyramidal geometry, the central atom is surrounded by five atoms. Trigonal bipyramidal geometry consists of two planes, one is axial and the other is equatorial. Three atoms are in the equatorial position and two are in the axial position. PF5 is the best example of this geometry. In PF5, The F-P-F angle between equatorial positions is 120 degrees, and between the axial and equatorial positions, it is 90 degrees. It is a lewis acid.



Leave a Reply